Bored piles are a very effective, state-of-the-art construction element with many applications in foundation and civil engineering.
Common uses
As heavy foundations, securing deep excavation especially close to existing buildings as well as stabilising and retaining slopes
In a variety of infrastructure projects such as tunnelling, road or bridge construction as well as flood protection
Transfer and withstand high loads
Retain ground alongside an excavation pit or close to adjacent buildings, often combined with other techniques such as ground anchors or soil nails
For slope stabilisation to prevent landslides, or protect existing buildings
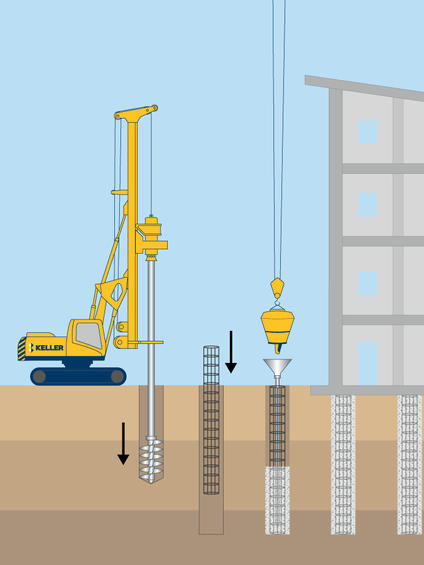
Process
A temporary casing is installed and soil drilled out using specialised tools. If the hole requires support to remain open, additional casing or drilling fluid can be used. Full length reinforcing steel is lowered into the hole which is then filled with concrete. Bored piles can be drilled to depths in excess of 60m and typical diameters range up to 2.4m.
Advantages
Can support high loads
Various diameters available from 450mm upwards
Minimal settlement and deformation
Minimum vibration
Quality assurance
We use a variety of quality assurance methods for our products including top down and integrity testing, bottom bi-directional pile load tests, and digital recording and logging of the execution parameters.